Design Pattern: Prompt Chaining
Prompt Chaining is a fundamental and effective design pattern for tackling complex tasks with LLMs in CozyUI. It involves breaking down a larger problem into a sequence of smaller, more manageable steps, where each step is handled by an LLM node, and the output of one LLM node becomes the input for the next.
TIP
Why bother with this? Generally LLMs produce better results when they only have to focus on a single task, instead of doing multiple tasks in one go.
What is Prompt Chaining?
Imagine you have a task that's a bit too complex for a single LLM prompt to handle reliably or with high quality. Instead of trying to craft one perfect, intricate prompt, you "chain" multiple LLM calls together.
- Step 1: The first LLM node takes an initial input and performs a specific sub-task (e.g., brainstorms ideas).
- Step 2: The output from the first LLM node is then fed as input to a second LLM node, which performs the next sub-task (e.g., refines one of the brainstormed ideas into a paragraph).
- Step 3 (and so on): This can continue for several steps, with each LLM focusing on a distinct part of the overall goal.
Optionally, between these LLM calls, you can insert other CozyUI nodes to perform checks, transformations, or decisions (acting as "gates") to ensure the process is on track or to modify the data before it goes to the next LLM.
Why Use Prompt Chaining?
The primary goal of prompt chaining is to trade off a bit of latency (time) for significantly higher accuracy, quality, and control over the final output.
- Improved Quality & Accuracy: Each LLM in the chain has a simpler, more focused task. This generally leads to better results for each sub-task, contributing to a higher quality overall output. It's often easier for an LLM to excel at one small thing than one very big, multi-faceted thing.
- Better Control & Iteration: You can inspect and validate the output at each step. If one part of the chain isn't performing well, you can focus on refining the prompt for just that specific LLM node without affecting the others.
- Handling Complexity: Decomposing a complex problem into smaller, sequential steps makes the overall logic easier to design, understand, and debug.
- Reduced Hallucinations/Errors: By giving each LLM a more constrained task, you can often reduce the likelihood of the model going off-topic or generating incorrect information.
When is Prompt Chaining a Good Fit?
This pattern is ideal for situations where:
- The overall task can be clearly and cleanly broken down into a fixed sequence of sub-tasks.
- Each sub-task can be effectively handled by a targeted LLM prompt.
- You need higher quality or more control than a single, complex prompt can provide.
- You're willing to accept a slightly longer processing time in exchange for better results.
Examples in CozyUI
Let's look at how you might implement prompt chaining in CozyUI.
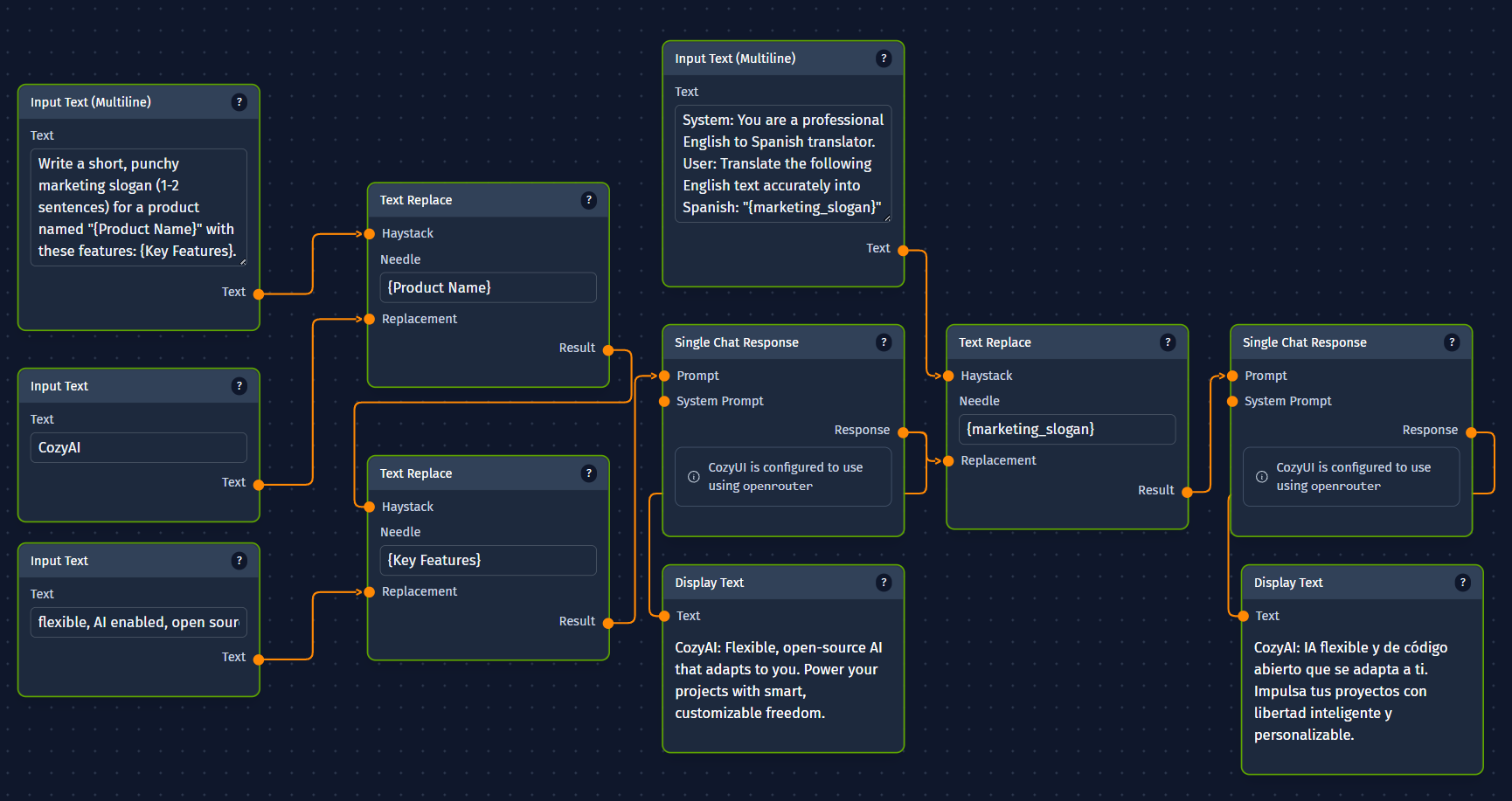
Example 1: Generating and Translating Marketing Copy
Goal: Create a short piece of marketing copy for a new product and then translate it into Spanish.
CozyUI Workflow:
Input TextNode (or similar):- Input: Product Name (e.g., "SuperWidget X")
- Input: Key Features (e.g., "Durable, Eco-friendly, Easy-to-use")
Single Chat ResponseNode (LLM 1 - Copywriter):- Input (Prompt): Takes Product Name and Key Features.
System: You are a creative marketing copywriter. User: Write a short, punchy marketing slogan (1-2 sentences) for a product named "{Product Name}" with these features: {Key Features}. - Output:
marketing_slogan(e.g., "Experience the SuperWidget X: Durability meets eco-friendly design for ultimate ease of use!")
- Input (Prompt): Takes Product Name and Key Features.
Single Chat ResponseNode (LLM 2 - Translator):- Input (Prompt): Takes
marketing_sloganfrom LLM 1.System: You are a professional English to Spanish translator. User: Translate the following English text accurately into Spanish: "{marketing_slogan}" - Output:
translated_slogan(e.g., "¡Experimenta el SuperWidget X: La durabilidad se une al diseño ecológico para una máxima facilidad de uso!")
- Input (Prompt): Takes
DisplayTextNode:- Input: Takes
translated_sloganto display the final result.
- Input: Takes
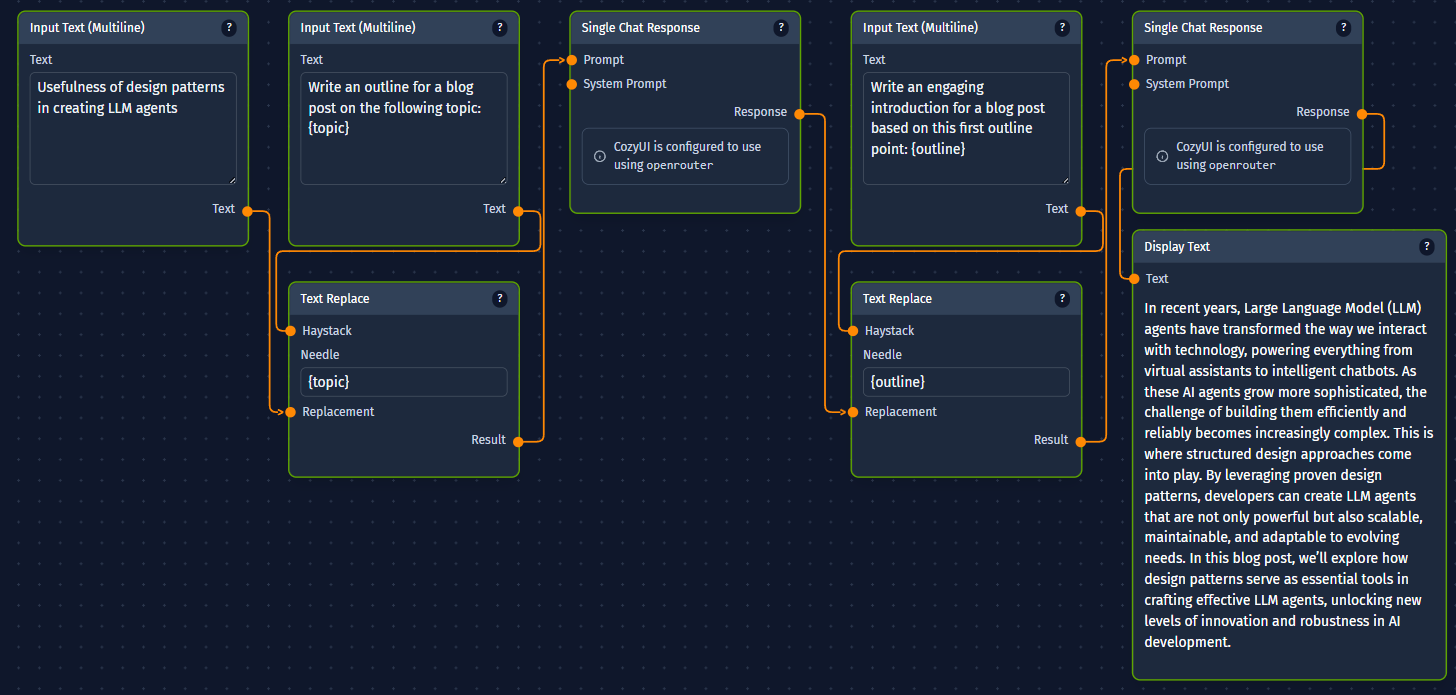
Example 2: Outline, Review, and Write Document Section
Goal: Generate an outline for a blog post, allow for a (simulated) review/gate, then write the introduction based on the (approved) outline.
CozyUI Workflow (Conceptual):
Input TextNode: Topic for the blog post.LLM Node(LLM 1 - Outliner): Generates a structured outline for the topic.- Output:
document_outline
- Output:
LLM Node(LLM 2 - Writer): Takes thedocument_outline(specifically, perhaps the first point of the outline).- Prompt: "Write an engaging introduction for a blog post based on this first outline point: {outline}."
- Output:
introduction_text
DisplayTextNode: Displaysintroduction_text.
General Advice for Prompt Chaining:
- Prompt Engineering: Each LLM node in the chain still requires careful prompt engineering for its specific sub-task.
- Error Handling: Consider what happens if an intermediate LLM call fails or produces unexpected output. You might add "gate" nodes (like
If Nodeor validation logic) to handle such cases. - Data Formatting: Ensure the output format of one LLM is suitable as input for the next. Sometimes a simple text node to reformat or extract specific parts might be needed in between.
- Latency: Be mindful that each LLM call adds to the total processing time. For very long chains, this can become significant.
- LLM Sizes: As the created prompts are more focused, you might be able to get away with using a smaller, cheaper model to get a similar quality answer for the subtasks.
Prompt chaining is a versatile pattern that forms the basis for many more advanced agentic behaviors. By mastering it, you can significantly enhance the capabilities and quality of your CozyUI workflows.